Overview
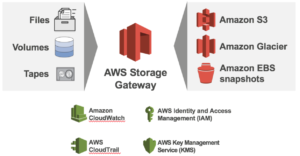
The storage gateway of AWS provides a simple way to integrate your on-premises storage with your AWS S3. It does this through the installation of a VM appliance in your VMware or Hyper-V implementation. You could also install it on to an EC2 instance in your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) infrastructure for a different modality.
Types of Storage Gateways
There are four total types of Storage Gateway (note that Volume Gateway consists of two variations):
- File gateway – this uses NFS and is for your flat files (PDFs, JPGs, etc)
- Volume gateway – this actually consists of stored volumes and cached volumes – this is for block storage using iSCSI
- Tape gateway – to create virtual tape libraries
While the volume gateway options both provide block storage (using iSCSI) and would be great for things like virtual hard disks and databases, note that the stored volume approach duplicates your data to the cloud while the cached volume approach only keeps cached copies of frequently accessed files in your on-premises location.
Common Use Cases
Customers commonly use Storage Gateway services for use cases such as:
- Hybrid cloud workloads – big data, cloud bursting or cloud data migration architectures may need local capacity and performance with a connection to a central storage repository in the cloud. Storage Gateway streamlines moving data between your organization and AWS to manage workloads in the cloud.
- Backup, archive, and disaster recovery – Storage Gateway is a drop-in replacement for tape and tape automation, and integrates with industry backup software packages. Storage Gateway can take snapshots of your local volumes which can restored as Amazon EBS volumes in the event of a local site disaster.
- Tiered Storage – some customers design storage architectures that preserve or extend high performance on-premises investments by adding a lower cost, on-demand cloud tier. This helps with archival or cost-reduction projects.
Want to learn more – this is from my latest CBT Nuggets course on AWS. This course is in development as I post this.